The past 10 years have seen a very fast development of supply chain management. Against this backdrop, what was a simple linear flow of the goods has now become a sophisticated, interdependent ecosystem of manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, regulators, and consumers. As trade and customer pressures intensify across the globe and the need to be more transparent increases, conventional supply chain systems are finding it hard to manage. This is the area where blockchain technology is becoming an empowering force of trust, visibility, and efficiency of operation in supply networks.
Blockchain is no longer considered to be linked only with cryptocurrencies. It is redefining the way data are captured, distributed, and checked in business today. In supply chain management it serves as a single source of the truth that can be trusted by all the stakeholders, and friction and uncertainty is minimized with every step in the process.
Understanding Blockchain Beyond the Hype
In its simplest form, blockchain is a distributed electronic registry authenticating transactions in more than one system in a secure and immutable manner. All transactions are time-stamped and checked by the participants in the network and are included in a chain of records that can never be changed in the future. This architecture eliminates the necessity of centralized control, and data integrity is preserved.
In the case of supply chains, this implies that information about the origin of the products, their shipping status, quality checks, and transfers of ownership can be stored permanently and accessed in real time. Blockchain development has become a viable strategy that many enterprises are looking into as a way of modernizing the stagnant supply chain processes and ensuring the sustainability of their operations in the long term.
Why Traditional Supply Chains Face Growing Challenges
The new supply chains are global, inter-temporal, and inter-regulative. Although globalization has enhanced scalability and cost reduction, it has also come with some such risks as data silos, counterfeit goods, shipment delays, and compliance failures.
One of the largest pain points includes the lack of end-to-end visibility. In case of fragmented data in more than one system, decision-makers can hardly react quickly to disruption. Paperwork, slowness in reporting, and poor incompatible data standards only contribute to more operational inefficiencies and loss of money.
Blockchain in supply chain management addresses these issues by enabling seamless data sharing while maintaining accountability among all participants.
Transparency and Trust Through Shared Ledgers
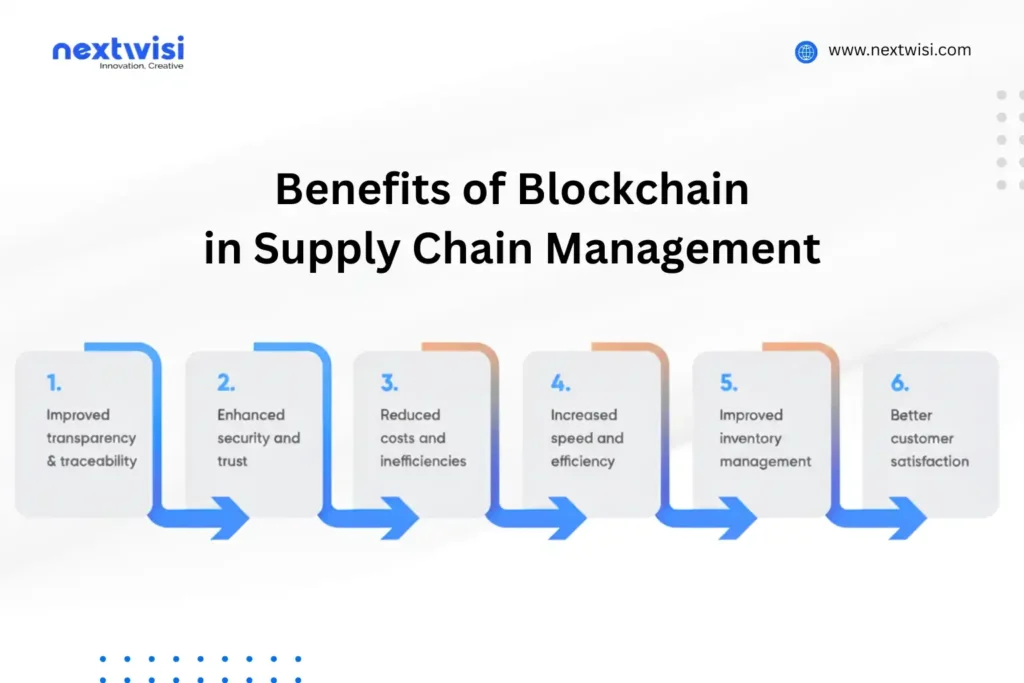
An efficient supply chain is based on transparency. Blockchain produces a common registry where all the authorised members can access the same validated data. This avoids conflict by having wrong records, and it fosters trust among partners that might not have a close relationship among themselves.
Blockchain solutions, when integrated with the newest cloud solutions, will be able to achieve scalability and provide real-time access to key supply chain data. The integration enables the businesses to track the shipments, inventory level, and the performance of the suppliers within one digital space and enhance coordination and responsiveness.
Enhancing Traceability From Source to Consumer
One of the most useful advantages of blockchain in supply chain management is traceability. The product can be traced back to the sourcing stage of raw material until the ultimate delivery stage, with all the stages being registered on the ledger. This is particularly significant with such industries as food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods, where the level of authenticity and safety is paramount.
With a full product history, any company can easily know the origin of defects, recalls can be handled better, and it can demonstrate compliance with the regulatory regulations. This is also beneficial to the consumers who get insight into the sources of products and their production, which enhances brand trust.
Automation and Operational Efficiency
Blockchain also allows automation, which is done by smart contracts, or self-executing contracts, which are activated by other conditions being satisfied. As an example, payment may be made automatically after delivery of goods and verification of goods, which will save time and administrative overheads.
Blockchain can be incorporated in digital ecosystems where the creation of apps is involved, as user-facing platforms can enable stakeholders to monitor the movements of shipments, authorize transactions, or get access to compliance information in real time. Such automation minimizes errors by humans and speeds up supply chain operations without loss of control.
Cost Reduction Across the Supply Network
Hidden costs that may arise due to inefficiencies in supply chains are usually excess inventory, manual reconciliation, and dispute resolution. Blockchain saves these costs by excluding the middlemen and paperwork.
This is because all parties operate on the same verified data , therefore the reconciliation process is cut drastically. This results in reduced operational costs, quicker turnaround time, and increased profitability in the long run. Financial implications of adopting blockchain in the long run may be high, particularly for large and multi-tier supply chains.
Supporting Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Businesses around the world have developed the concept of sustainability as a priority. Blockchain assists organizations to monitor their supply chains in the areas of environmental impact, ethical sourcing, and labor practices. Authenticated information simplifies reporting sustainability measures and achievement of ESG.
Companies can ensure that they act responsibly and prevent greenwashing by storing the carbon footprint, the origins of the materials, and the certifications of suppliers in a blockchain. Such openness builds trust and helps in long-term brand value amongst the stakeholders.
Security and Data Integrity Advantages
The safety of blockchain is ensured by the decentralized structure and cryptographical authentication. After data is written, it cannot be changed without the agreement of the network, and it becomes incredibly hard to commit fraud and modify data.
Such immutability is especially useful in the supply chains where the accuracy of data is vital. Blockchain will preserve information integrity in the product lifecycle, either through quality assurance records or custom documentation.
Challenges to Consider Before Implementation
Although blockchain has its benefits, such adoption does not come without difficulties. The process of integrating with the legacy systems may be complicated, and large volumes of transactions still pose a challenge of scalability. Legal and regulatory uncertainty is also possible, as blockchain standards are still developing around the world.
In order to successfully implement, the correct blockchain framework must be selected, supply chain partners need to collaborate, and it has to be carefully planned. Companies also need to invest in competencies and forms of governance to operate blockchain networks successfully.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
The digital, interconnected, and data-driven supply chain management is the future. Blockchain will become a key factor in making ecosystems transparent where the trust is embedded in the system instead of being imposed by means of manual controls.
With more people using it, blockchain will become more intertwined with IoT, analytics, and automation tools, providing more business opportunities and efficiency incentives. Building more resilient and flexible supply chains will provide early adopters with a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Blockchain in supply chain management is reshaping how businesses manage data, logistics, and partnerships. From improved traceability and security to cost reduction and sustainability, the long-term value of blockchain adoption is clear.
Experienced technology partners should be involved in the implementation of the secure and scalable blockchain solutions by companies willing to do it. One such company is Nextwisi Solutions, which offers professional blockchain development solutions to assist businesses in designing, implementing, and optimizing blockchain-based supply chain systems that are customized to the needs of real-life business operations.



